Where can you find the latest Cisco 300-115 dumps exam materials? Latest useful Cisco CCDP 300-115 dumps exam practice questions and answers free download from leads4pass. The best helpful Cisco CCDP 300-115 dumps pdf materials and vce youtube demo update free shared. “Implementing Cisco IP Switched Networks” is the name of Cisco CCDP https://www.leads4pass.com/300-115.html exam dumps which covers all the knowledge points of the real Cisco CCDP. High quality latest Cisco CCDP 300-115 dumps pdf training resources and study guides update free try, 100% success and guarantee to pass Cisco 300-115 exam test easily at the first time.
Latest Cisco 300-115 dumps pdf materials free download: https://drive.google.com/open?id=0B_7qiYkH83VROUdnZWRYLTJta1E
Latest Cisco 400-351 dumps pdf materials free download: https://drive.google.com/open?id=0B_7qiYkH83VRV1NkNFZ3SW80UVU

New Cisco CCDP 300-115 dumps exam questions and answers (1-10)
QUESTION 1
What is the maximum number of switches that can be stacked using Cisco StackWise?
A. 4
B. 5
C. 8
D. 9
E. 10
F. 13
Correct Answer: D
Explanation:
Up to 9 Cisco Catalyst switches can be stacked together to build single logical StackWise switch since Cisco IOS XE Release 3.3.0SE. Prior to Cisco IOS XE Release3.3.0SE, up to 4 Cisco Catalyst switches could be stacked together.
QUESTION 2
A network engineer wants to add a new switch to an existing switch stack. Which configuration must be added to the new switch before it can be added to the switch stack?
A. No configuration must be added.
B. stack ID
C. IP address
D. VLAN information
E. VTP information
Correct Answer: A
Explanation:
Switch Stack Offline Configuration
You can use the offline configuration feature to provision (to supply a configuration to) a new switch before it joins the switch stack. You can configure in advance the stack member number, the switch type, and the inter- faces associated with a switch that is not currently part of the stack. The configuration that you create on the switch stack is called the provisioned configuration . The switch that is added to the switch stack and that re- ceives this configuration is called the provisioned switch.
You manually create the provisioned configuration through the switch stack-member-number provision type global configuration command. The provisioned configuration is automatically created when a switch is added to a switch stack and when no provisioned configuration exists.
When you configure the interfaces associated with a provisioned switch (for example, as part of a VLAN), the switch stack accepts the configuration, and the information appears in the running configuration. The interface associated with the provisioned switch is not active, operates as if it is administratively shut down, and the no shutdown interface configuration command does not return it to active service. The interface associated with the provisioned switch does not appear in the display of the specific feature; for example, it does not appear in the show vlan user EXEC command output.
The switch stack retains the provisioned configuration in the running configuration whether or not the provi- sioned switch is part of the stack. You can save the provisioned configuration to the startup configuration file by entering the copy running-config startup-config privileged EXEC command. The startup configuration file ensures that the switch stack can reload and can use the saved information whether or not the provisioned switch is part of the switch stack.
Effects of Adding a Provisioned Switch to a Switch Stack
When you add a provisioned switch to the switch stack, the stack applies either the provisioned configuration or the default configuration. Table 5-1 lists the events that occur when the switch stack compares the provisioned configuration with the provisioned switch.
Table 5-1 Results of Comparing the Provisioned Configuration with the Provisioned Switch Scenario Result
The stack member num- 1. If the stack member number The switch stack applies bers and the switch types of the provisioned switch the provisioned configuramatch. matches the stack member num- tion to the provisioned ber in the provisioned configura- switch and adds it to the tion on the stack, and stack.
2. If the switch type of the provisioned switch matches the switch type in the provisioned configuration on the stack.
The stack member num- 1. If the stack member number The switch stack applies bers match but the switch of the provisioned switch the default configuration to types do not match. matches the stack member num- the provisioned switch and ber in the provisioned configuration on the stack, but adds it to the stack.
2. The switch type of the provi- The provisioned configura- sioned switch does not match the tion is changed to reflect switch type in the provisioned the new information.
configuration on the stack.
The stack member num- The switch stack applies ber is not found in the pro- the default configuration to visioned configuration. the provisioned switch and adds it to the stack.
The provisioned configuration is changed to reflect the new information.
The stack member num- The stack master assigns a new The switch stack applies ber of the provisioned stack member number to the pro- the provisioned configura- switch is in conflict with an visioned switch. tion to the provisioned existing stack member. switch and adds it to the The stack member numbers and stack.
QUESTION 3
What percentage of bandwidth is reduced when a stack cable is broken?
A. 0
B. 25
C. 50
D. 75
E. 100
Correct Answer: C
Explanation:
Physical Sequential Linkage
The switches are physically connected sequentially, as shown in Figure 3. A break in any one of the cables will result in the stack bandwidth being reduced to half of its full capacity. 300-115 dumps Subsecond timing mechanisms detect traffic problems and immediately institute failover. This mechanism restores dual path flow when the timing mechanisms detect renewed activity on the cable.
Figure 3. Cisco StackWise Technology Resilient Cabling

QUESTION 4
Refer to the exhibit.
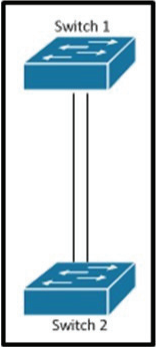
Which set of configurations will result in all ports on both switches successfully bundling into an EtherChannel?
A. switch1
channel-group 1 mode active
switch2
channel-group 1 mode auto
B. switch1
channel-group 1 mode desirable
switch2
channel-group 1 mode passive
C. switch1
channel-group 1 mode on
switch2
channel-group 1 mode auto
D. switch1
channel-group 1 mode desirable
switch2
channel-group 1 mode auto
Correct Answer: D
Explanation:
The different etherchannel modes are described in the table below:
Mode Description
active Places an interface into an active negotiating state, in which the interface starts negotiations with other interfaces by sending LACP packets.
auto Places an interface into a passive negotiating state, in which the interface re- sponds to PAgP packets it receives but does not start PAgP packet negotiation. This setting minimizes the transmission of PAgP packets.
desirable Places an interface into an active negotiating state, in which the interface starts negotiations with other interfaces by sending PAgP packets.
on Forces the interface into an EtherChannel without PAgP or LACP. With the on mode, a usable EtherChannel exists only when an interface group in the on mode is connected to another interface group in the on mode.
passive Places an interface into a passive negotiating state, in which the interface re- sponds to LACP packets that it receives, but does not start LACP packet negotiation. This setting minimizes the transmission of LACP packets.
Both the auto and desirable PAgP modes allow interfaces to negotiate with partner interfaces to determine if they can form an EtherChannel based on criteria such as interface speed and, for Layer 2 EtherChannels, trunking state and VLAN numbers.
Interfaces can form an EtherChannel when they are in different PAgP modes as long as the modes are compatible. For example:
– An interface in the desirable mode can form an EtherChannel with another interface that is in the desirable or auto mode.
– An interface in the auto mode can form an EtherChannel with another interface in the desirable mode.
An interface in the auto mode cannot form an EtherChannel with another interface that is also in the auto mode because neither interface starts PAgP negotiation.
An interface in the on mode that is added to a port channel is forced to have the same characteristics as the already existing on mode interfaces in the channel.
QUESTION 5
Refer to the exhibit.

How can the traffic that is mirrored out the GigabitEthernet0/48 port be limited to only traffic that is received or transmitted in VLAN 10 on the GigabitEthernet0/1 port?
A. Change the configuration for GigabitEthernet0/48 so that it is a member of VLAN 10.
B. Add an access list to GigabitEthernet0/48 to filter out traffic that is not in VLAN 10.
C. Apply the monitor session filter globally to allow only traffic from VLAN 10.
D. Change the monitor session source to VLAN 10 instead of the physical interface.
Correct Answer: C
Explanation:
To start a new flow-based SPAN (FSPAN) session or flow-based RSPAN (FRSPAN) source or destination session, or to limit (filter) SPAN source traffic to specific VLANs, use the monitor session filter global configuration command.
Usage Guidelines
You can set a combined maximum of two local SPAN sessions and RSPAN source sessions. You can have a total of 66 SPAN and RSPAN sessions on a switch or switch stack. 300-115 dumps You can monitor traffic on a single VLAN or on a series or range of ports or VLANs. You select a series or range of VLANs by using the [ , | -] options.
If you specify a series of VLANs, you must enter a space before and after the comma. If you specify a range of VLANs, you must enter a space before and after the hyphen ( -). VLAN filtering refers to analyzing network traffic on a selected set of VLANs on trunk source ports. By default, all VLANs are monitored on trunk source ports. You can use the monitor session session_number filter vlan vlan-id command to limit SPAN traffic on trunk source ports to only the specified VLANs.
VLAN monitoring and VLAN filtering are mutually exclusive. If a VLAN is a source, VLAN filtering cannot be enabled. If VLAN filtering is configured, a VLAN cannot become a source.
QUESTION 6
Refer to the exhibit.
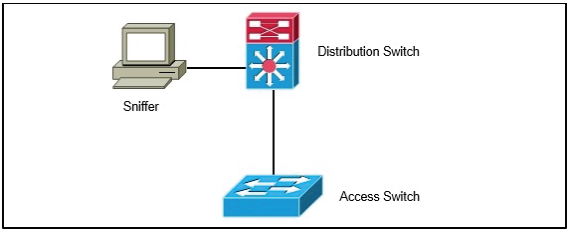
A network engineer wants to analyze all incoming and outgoing packets for an interface that is connected to an access switch. Which three items must be configured to mirror traffic to a packet sniffer that is connected to the distribution switch? (Choose three.)
A. A monitor session on the distribution switch with a physical interface as the source and the remote SPAN VLAN as the destination
B. A remote SPAN VLAN on the distribution and access layer switch
C. A monitor session on the access switch with a physical interface source and the remote SPAN VLAN as the destination
D. A monitor session on the distribution switch with a remote SPAN VLAN as the source and physical interface as the destination
E. A monitor session on the access switch with a remote SPAN VLAN source and the physical interface as the destination
F. A monitor session on the distribution switch with a physical interface as the source and a physical interface as the destination
Correct Answer: BCD
Explanation:
You can analyze network traffic passing through ports or VLANs by using SPAN or RSPAN to send a copy of the traffic to another port on the switch or on another switch that has been connected to a network analyzer or other monitoring or security device. SPAN copies (or mirrors) traffic received or sent (or both) on source ports or source VLANs to a destination port for analysis.
RSPAN supports source ports, source VLANs, and destination ports on different switches (or different switch stacks), enabling remote monitoring of multiple switches across your network. The traffic for each RSPAN session is carried over a user-specified RSPAN VLAN that is dedicated for that RSPAN session in all participating switches. The RSPAN traffic from the source ports or VLANs is copied into the RSPAN VLAN and forwarded over trunk ports carrying the RSPAN VLAN to a destination session monitoring the RSPAN VLAN. Each RSPAN source switch must have either ports or VLANs as RSPAN sources. The destination is always a physical port.
QUESTION 7
After an EtherChannel is configured between two Cisco switches, interface port channel 1 is in the down/down state. Switch A is configured with channel-group 1 mode active, while Switch B is configured with channel-group 1 mode desirable. Why is the EtherChannel bundle not working?
A. The switches are using mismatched EtherChannel negotiation modes.
B. The switch ports are not configured in trunking mode.
C. LACP priority must be configured on both switches.
D. The channel group identifier must be different for Switch A and Switch B.
Correct Answer: A
Explanation:
Here we have a situation where one switch is using active mode, which is an LACP mode, and the other is using desirable, which is a PAGP mode. You can not mix the LACP and PAGP protocols to form an etherchannel. Here is a summary of the various etherchannel modes:
EtherChannel PAgP Modes
Mode Description
auto Places a port into a passive negotiating state, in which the port responds to PAgP packets it receives but does not start PAgP packet negotiation. This setting minimizes the transmission of PAgP packets.
This mode is not supported when the EtherChannel members are from differ- ent switches in the switch stack (cross-stack EtherChannel).
desirable Places a port into an active negotiating state, in which the port starts negotia- tions with other ports by sending PAgP packets.
This mode is not supported when the EtherChannel members are from differ- ent switches in the switch stack (cross-stack EtherChannel).
EtherChannel LACP Modes
Mode Description
active Places a port into an active negotiating state in which the port starts negotia- tions with other ports by sending LACP packets.
passive Places a port into a passive negotiating state in which the port responds to LACP packets that it receives, but does not start LACP packet negotiation. This setting minimizes the transmission of LACP packets.
QUESTION 8
An EtherChannel bundle has been established between a Cisco switch and a corporate web server. The network administrator noticed that only one of the EtherChannel links is being utilized to reach the web server. What should be done on the Cisco switch to allow for better EtherChannel utilization to the corporate web server?
A. Enable Cisco Express Forwarding to allow for more effective traffic sharing over the EtherChannel bundle.
B. Adjust the EtherChannel load-balancing method based on destination IP addresses.
C. Disable spanning tree on all interfaces that are participating in the EtherChannel bundle.
D. Use link-state tracking to allow for improved load balancing of traffic upon link failure to the server.
E. Adjust the EtherChannel load-balancing method based on source IP addresses.
Correct Answer: E
Explanation:
EtherChannel load balancing can use MAC addresses, IP addresses, or Layer 4 port numbers, and either source mode, destination mode, or both. 300-115 dumps The mode you select applies to all EtherChannels that you configure on the switch. Use the option that provides the greatest variety in your configuration. For example, if the traffic on a channel only goes to a single MAC address (which is the case in this example, since all traffic is going to the same web server), use of the destination MAC address results in the choice of the same link in the channel each time. Use of source addresses or IP addresses can result in a better load balance.
QUESTION 9
Interface FastEthernet0/1 is configured as a trunk interface that allows all VLANs. This command is configured globally:
monitor session 2 filter vlan 1 – 8, 39, 52
What is the result of the implemented command?
A. All VLAN traffic is sent to the SPAN destination interface.
B. Traffic from VLAN 4 is not sent to the SPAN destination interface.
C. Filtering a trunked SPAN port effectively disables SPAN operations for all VLANs.
D. The trunk’s native VLAN must be changed to something other than VLAN 1.
E. Traffic from VLANs 1 to 8, 39, and 52 is replicated to the SPAN destination port.
Correct Answer: E
Explanation:
The “monitor session filter” command is used to specify which VLANS are to be port mirrored using SPAN. This example shows how to monitor VLANs 1 through 5 and VLAN 9 when the SPAN source is a trunk interface:
Switch(config)# monitor session 2 filter vlan 1 – 5 , 9
QUESTION 10
A network engineer notices inconsistent Cisco Discovery Protocol neighbors according to the diagram that is provided. The engineer notices only a single neighbor that uses Cisco Discovery Protocol, but it has several routing neighbor relationships. What would cause the output to show only the single neighbor?
A. The routers are connected via a Layer 2 switch.
B. IP routing is disabled on neighboring devices.
C. Cisco Express Forwarding is enabled locally.
D. Cisco Discovery Protocol advertisements are inconsistent between the local and remote devices.
Correct Answer: A
Explanation:
If all of the routers are connected to each other using a layer 2 switch, then each router will only have the single switch port that it connects to as its neighbor.
Even though multiple routing neighbors can be formed over a layer 2 network, only the physical port that it connects to will be seen as a CDP neighbor. CDP can be used to determine the physical topology, but not necessarily the logical topology.
What Our Customers Are Saying:
Click here to have a review about us: https://www.resellerratings.com/store/leads4pass
High quality Cisco CCDP 300-115 dumps exam practice materials in PDF format free download from leads4pass. It is the best choice for you to pass Cisco 300-115 dumps exam. The best and most updated latest Cisco CCDP https://www.leads4pass.com/300-115.html dumps pdf training resources which are the best for clearing 300-115 exam test, and to get certified by Cisco CCDP, free download with high pass rate.
Best Cisco CCDP 300-115 dumps vce youtube demo: https://youtu.be/wyXFLuYtFpI
Why Choose Lead 4 Pass?
leads4pass is the best IT learning material provider. Other brands started early, the questions are outdated and it is very expensive. leads4pass provide the newest and cheapest practice questions and answers. leads4pass is the correct choice for IT learning materials, help you pass your exam easily.
